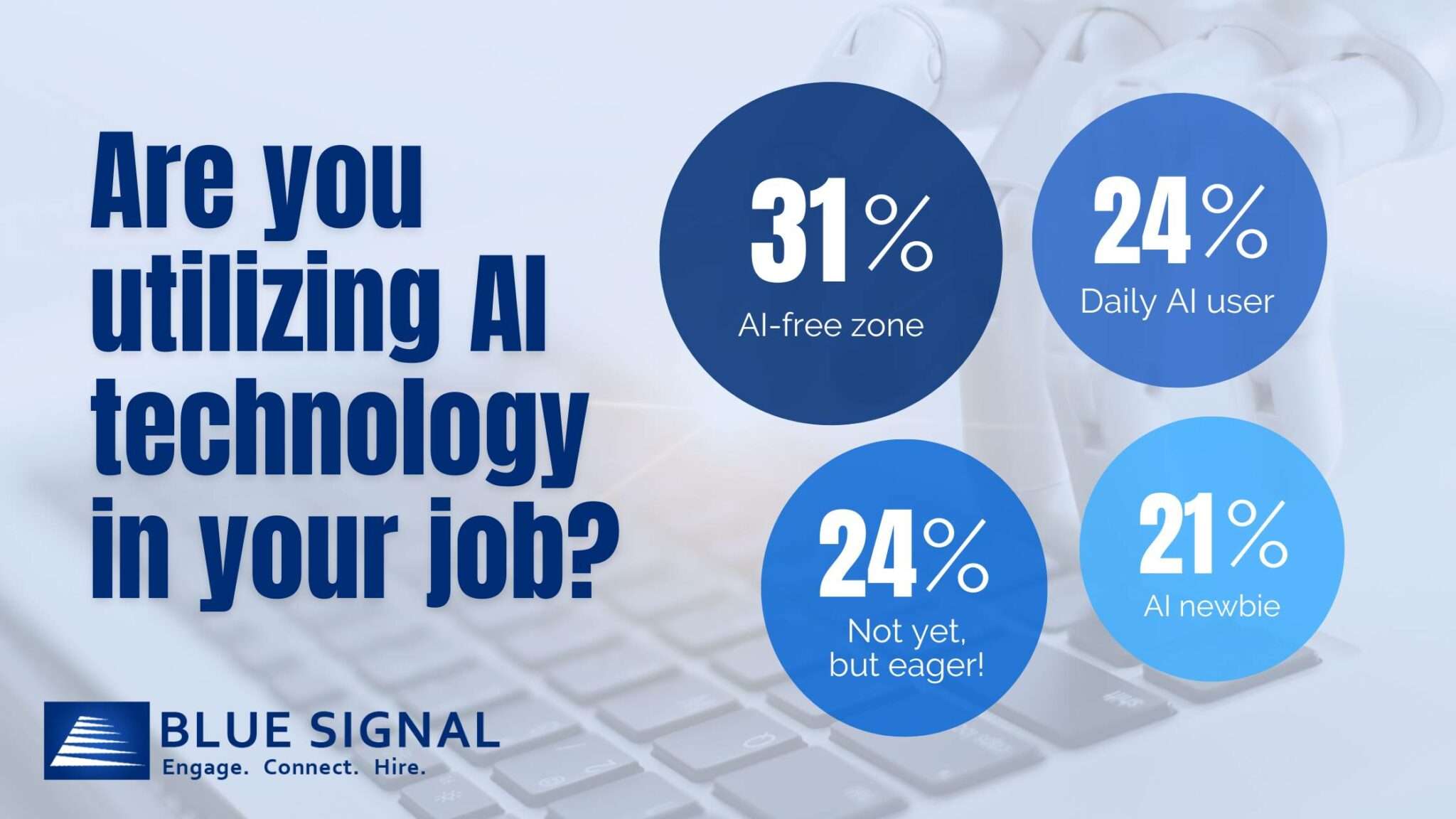
The digital age has brought about a myriad of innovations, but none have been as groundbreaking as the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). Recent LinkedIn polls conducted by Blue Signal provide a snapshot of the growing influence of AI in the workplace. Out of the respondents, 27% are actively using AI to enhance their products and services, while 19% are in the testing phase. This indicates a significant shift towards AI adoption across various sectors. As businesses continue to integrate AI, they're discovering new ways to optimize processes, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Individual Experiences with AI: A Closer Look
Diving deeper into individual experiences, the poll reveals a fascinating landscape of AI in the workplace. A quarter of the respondents use AI daily, suggesting a seamless integration of AI tools in their tasks. Meanwhile, 21% are just beginning their AI journey, eager to explore its potential. Another 24% are on the cusp of integrating AI, indicating a rapid adoption rate in the near future. This growing reliance on AI technologies underscores their transformative potential in daily operations.
The varied experiences of individuals with AI highlight the adaptability and versatility of AI tools. The spectrum of AI usage is vast from seasoned professionals harnessing advanced AI algorithms to novices exploring basic AI functionalities. This diversity in AI adoption is a testament to its potential to cater to a wide range of needs and skill levels.
Industry Trends: The AI Influence
AI's influence isn't limited to individual experiences. On a broader scale, industry trends are being shaped by the rise of AI in the workplace. The poll results revealed that smart automation and robotics, often powered by AI, influence 30% of the respondents' hiring decisions. This is closely followed by 5G & next-gen connectivity and sustainable practices. As industries evolve, AI-driven solutions are becoming the cornerstone of modern business strategies, reshaping traditional models and setting new benchmarks.
The transformative power of AI is evident across various sectors. From healthcare leveraging AI for personalized treatments to finance using AI for risk assessment, the applications are endless. A McKinsey report suggests that AI's influence will only grow, potentially creating new job roles while displacing others.
Decoding the Implications of AI Adoption
The surge in AI adoption paints a vivid picture of its implications. AI in the workplace is not just a trend; it's a transformative force. Businesses are leveraging AI to enhance product quality, streamline operations, and gain a competitive edge. However, with great power comes great responsibility. Companies must ensure ethical AI practices, prioritize transparency, and focus on continuous learning to harness AI's full potential.
As AI becomes more integrated into business operations, companies face the challenge of balancing innovation with ethics. Ensuring data privacy, avoiding biases in AI algorithms, and promoting transparency are crucial. A study by PwC emphasizes the need for businesses to adopt a responsible approach to AI, ensuring its benefits are realized while mitigating potential risks.
The AI Talent Race: A Recruiting Perspective
The integration of AI in the workplace has profound implications for the recruiting and staffing industry. As AI becomes more prevalent, there's a surging demand for AI-savvy candidates. Staffing agencies, like Blue Signal, are at the forefront of this talent race. They play a pivotal role in bridging the talent gap, ensuring companies have access to candidates adept at navigating the AI-driven landscape. For businesses looking to tap into the AI talent pool, Blue Signal's AI recruiting page offers a wealth of information and resources.
The demand for AI expertise is not limited to tech roles. From marketing to finance, AI skills are becoming increasingly valuable across various domains. As AI continues to permeate various sectors, recruiters face the challenge of sourcing candidates who not only have the technical know-how but also the ability to apply AI strategically. For a deeper dive into the impact of AI on recruiting, check out this insightful blog post by Blue Signal.
Preparing for an AI-Driven Future
The future is undeniably AI-driven. As AI continues to evolve, its role in the workplace becomes even more pronounced. Companies must stay ahead of the curve, investing in AI training and development. This not only ensures competitiveness but also prepares their workforce for the inevitable AI revolution. Embracing AI means unlocking new avenues of growth, innovation, and efficiency.
The Competitive Edge with AI
Companies that have already integrated AI into their operations are witnessing transformative results. From automating mundane tasks to providing data-driven insights, AI is proving to be a game-changer. Businesses that leverage AI tools and platforms are better positioned to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and deliver enhanced customer experiences. In a rapidly evolving market, having an AI-driven approach provides a significant competitive advantage.

Preparing the Workforce for AI
While AI brings numerous benefits, it also necessitates a shift in the skill sets required in the workplace. Continuous learning and upskilling become paramount. Companies need to invest in training programs that equip their employees with the knowledge and skills to work alongside AI tools. This not only boosts employee confidence but also ensures that they remain relevant in an AI-augmented environment.
AI in Recruiting: The Future is Now
As highlighted in our previous article, AI is revolutionizing the recruiting industry. At Blue Signal, we leverage AI to match candidates with the perfect job opportunities, ensuring that both companies and job seekers benefit from this technological advancement. The integration of AI in recruiting processes ensures faster, more accurate matches, and a streamlined hiring process.
Conclusion
The rise of AI in the workplace is not a fleeting trend; it's the future of work. As businesses, professionals, and recruiters, embracing this change is essential. By understanding the implications of AI, investing in training, and leveraging the power of AI in operations and recruiting, companies can ensure they are not only prepared for the future but are also leading the way.
Partner with us for your next hire.
Set up a free consultation with a recruiting manager. Tell us about your hiring need.
By submitting this form, you consent to receive communications from Blue Signal, including phone calls, emails, and text messages.

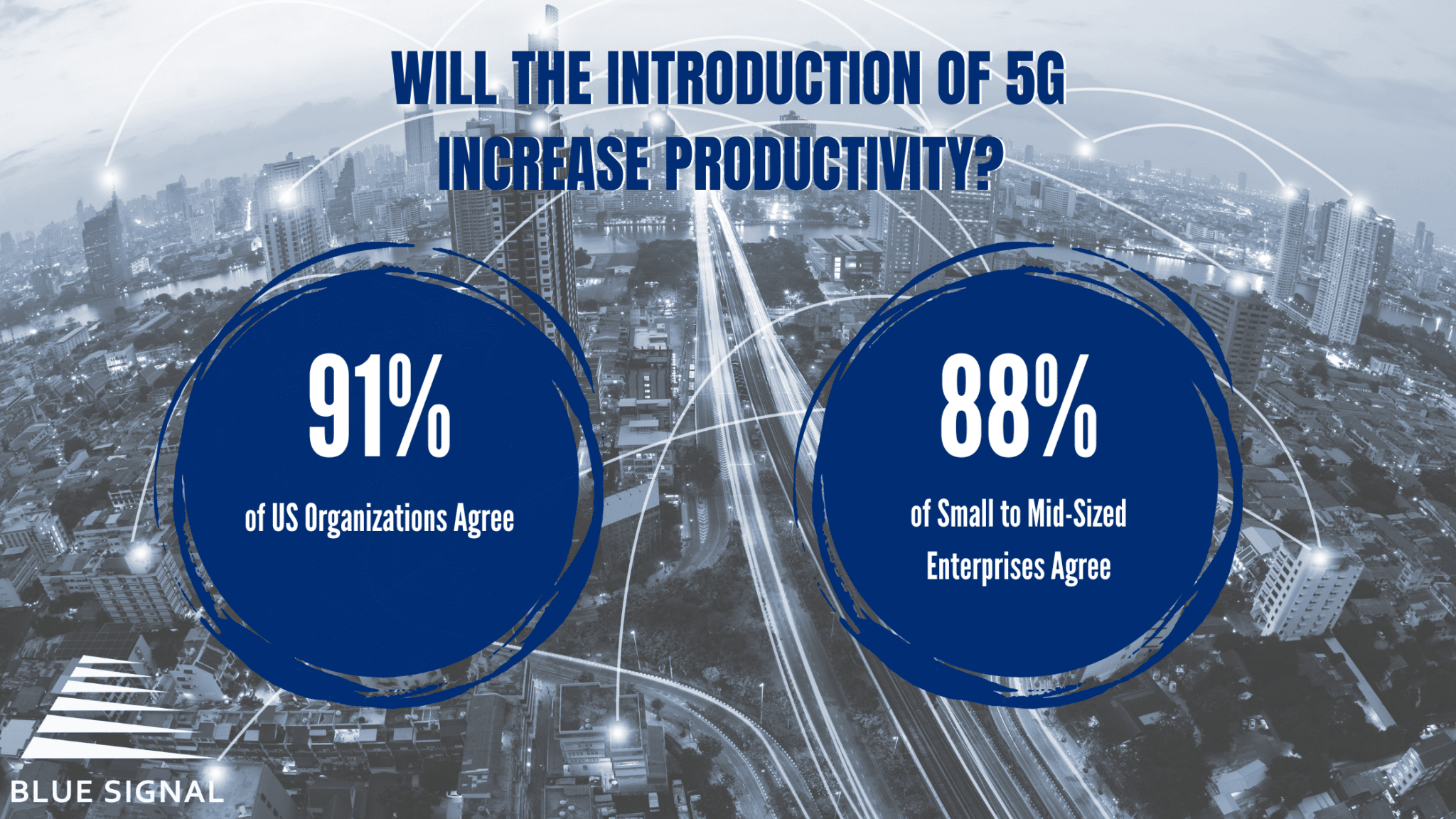
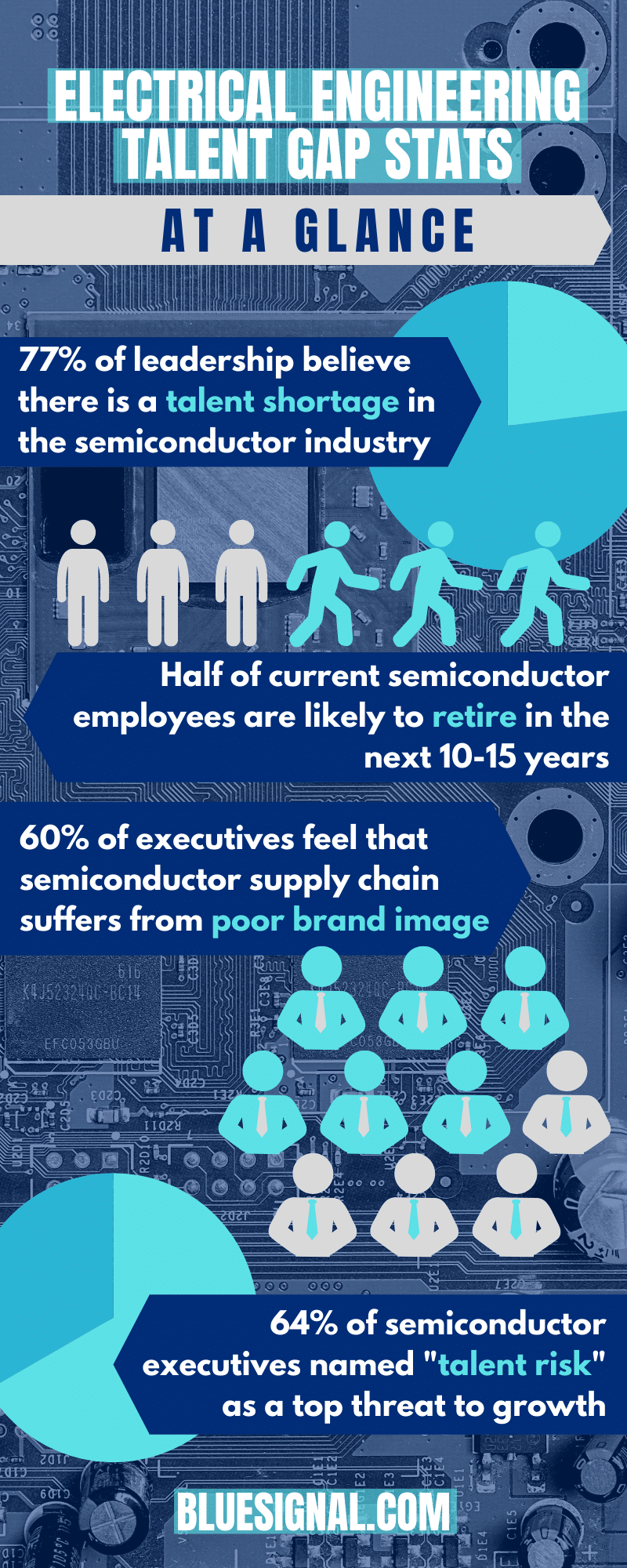
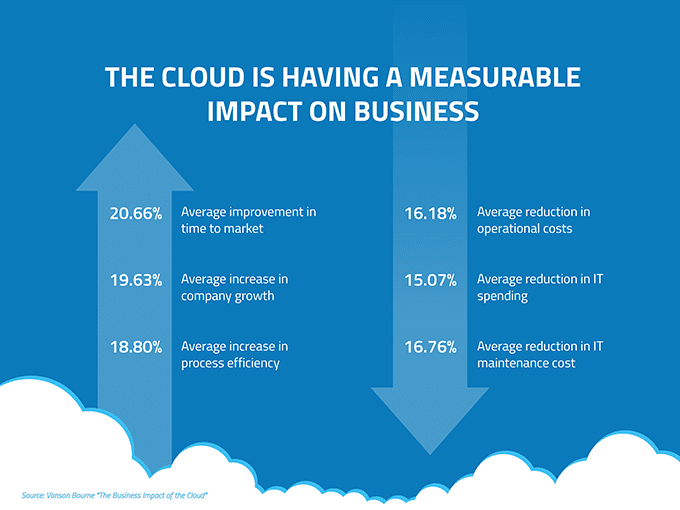


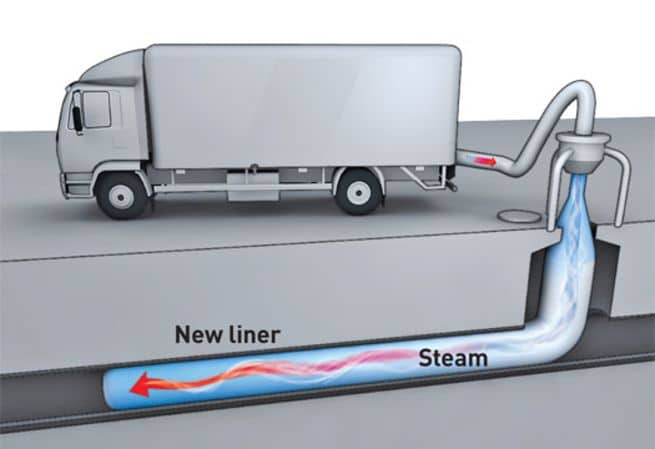


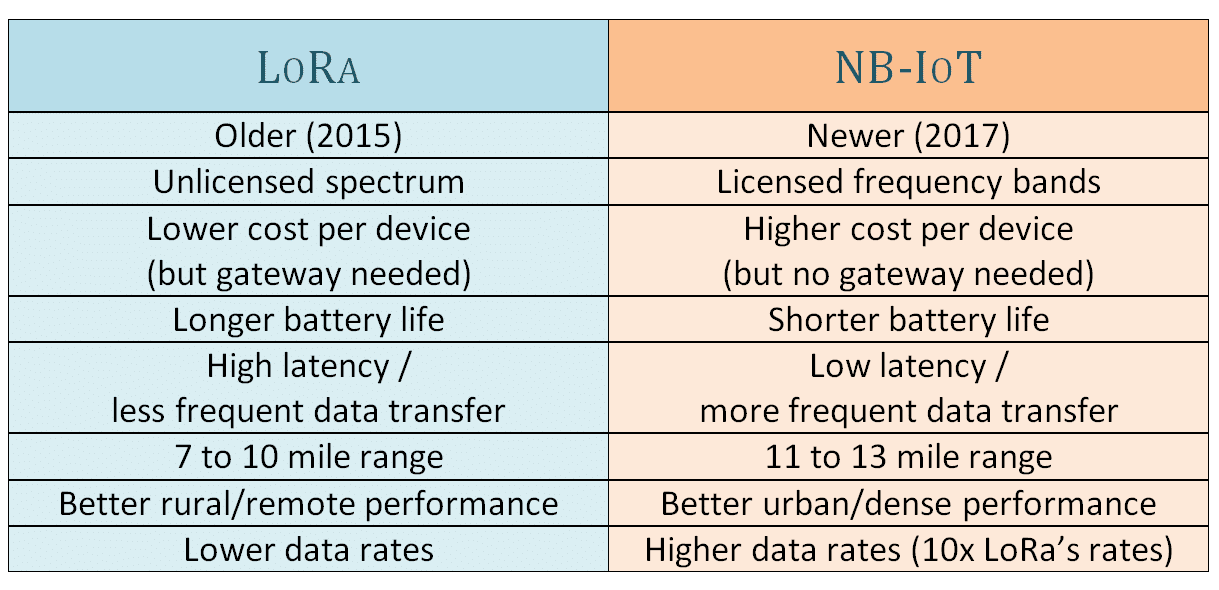
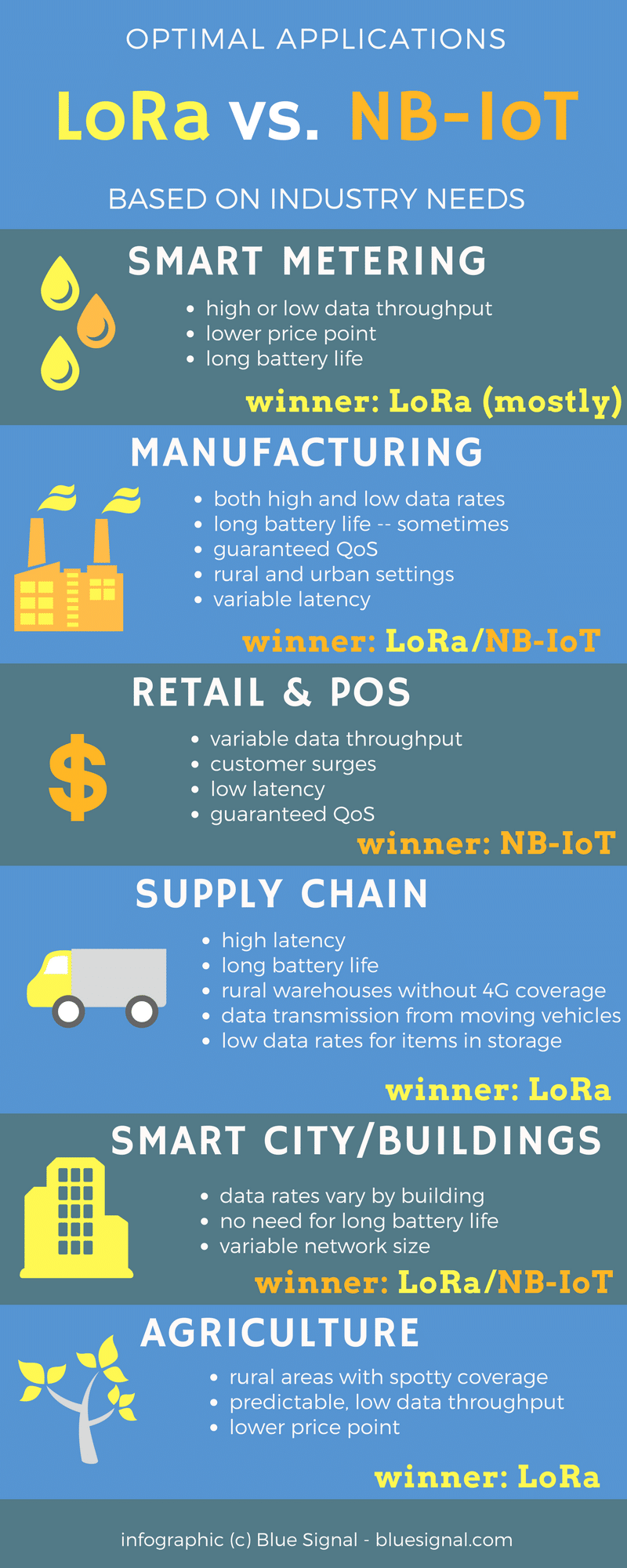
 LPWAN stands for Low-Power Wide Area Network, a wireless network designed to efficiently connect smart devices across long distances, usually through a low bit rate. LPWANs are ideal for IoT devices that don’t need to manage large amounts of data, or for circumventing more expensive gateway technology. This can include smart meters, consumer products, and sensors. The overall value of the LPWAN market is expected to reach $25 billion within 4 years.
LPWAN stands for Low-Power Wide Area Network, a wireless network designed to efficiently connect smart devices across long distances, usually through a low bit rate. LPWANs are ideal for IoT devices that don’t need to manage large amounts of data, or for circumventing more expensive gateway technology. This can include smart meters, consumer products, and sensors. The overall value of the LPWAN market is expected to reach $25 billion within 4 years.