By now you’ve probably caught the buzz about this thing called 5G that’s coming to change the world… but what is it really? And what will it mean for your business once it’s here? 5G is the 5th generation mobile network and the new global wireless standard. 5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps data speeds, much lower latency, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users across the globe. Simply put, it’ll make your mobile connectivity faster and more reliable. This technology is a huge breakthrough in wireless tech and some industry insiders have gone so far as to say that the 5G network will be as revolutionary as the printing press, the automobile, and electricity. So the question is, have you thought about how your business will change? In this blog, we’re hitting on all the key features of 5G that will revolutionize the way you do business and how to utilize them most effectively.
Ability to Work From Anywhere
With the recent pandemic and the majority of the nation’s workforce working from home, the capability to connect wirelessly, from any location is more necessary than ever. 5G enables just that; making being chained to an Ethernet cable or within range of a Wi-Fi hotspot a thing of the past. With the power of 5G, users will be able to connect to high-speed connections from just about anywhere. Yes, anywhere. A recent study shows 62% of employees work remotely at least part-time and this number only continues to rise as more employers continue to enforce health and safety precautions. With the abilities of 5G, businesses will be able to allow even more flexibility to their employees when it comes to working locations. In turn, this creates a larger candidate pool as geographical location ceases to be a qualifier for employees. This ease of accessibility is sure to increase morale and create a more relaxed workforce.
Seamless Functionality
With 5G, not only will the connection be vastly available but the functionality will be seamless. Through its fluid capabilities, 5G allows not just remote work but virtual work. The difference? Users will be able to access data, communicate with co-workers, collaborate on projects just as seamlessly as if they were physically in the same room. Remote workers will no longer be held back by needing access to large amounts of data, or a brainstorming session interrupted by poor video connection and lag. Further, with the increased capability, running more advanced technology becomes a breeze. Businesses will be able to access and implement virtual reality, augmented reality, and AI technology into their typical work routines creating a more connected and technologically advanced environment.
Increased Productivity
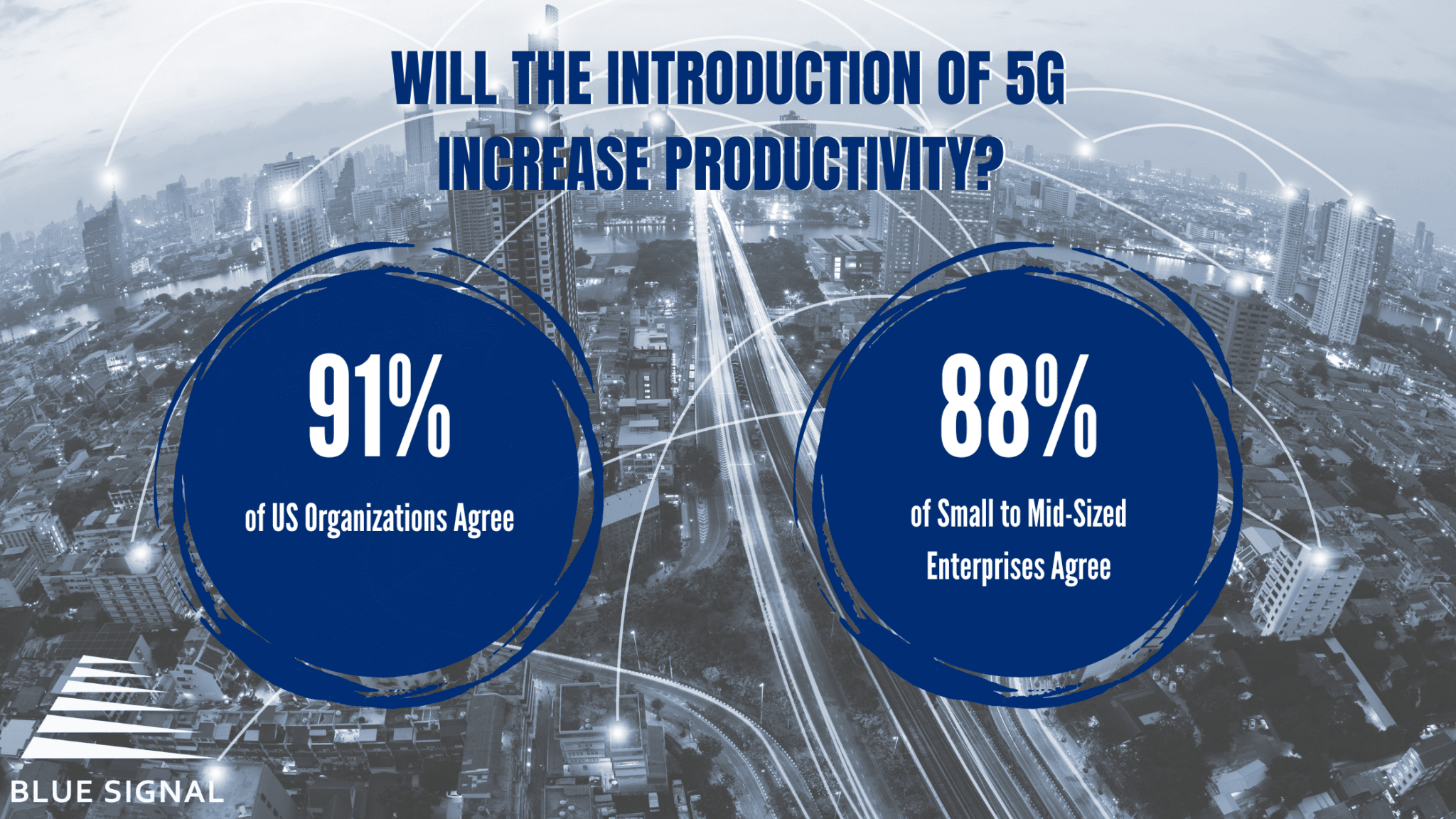
The entire workforce is buzzing in anticipation of the impact 5G will have on the way we function. 91% of US organizations and 88% of small to mid-sized enterprises agree that 5G will increase productivity. As mentioned earlier, lagging connections and download speeds can really disrupt remote and in-office employees’ workflow and attention span. Significantly faster data speeds mean far lower latency while waiting for a file to load, a meeting to start, attachments to download, etc. A big contributor to slow or glitchy connections is an influx of users in a centralized area. 5G allows for up to a million devices per square kilometer, making high-speed connections seamless even in extremely high traffic areas. There is an overwhelming amount of both large and small impacts that will contribute to maximized productivity from every angle. Even something as small as improved energy efficiency will result in prolonged battery life on devices, eliminating time searching for a lost charger or an outlet in a crowded coffee shop.
Improve Company Communication & Culture
Especially in the current state of the world, having a strong company culture is more important than ever to keep employees engaged. Human connection and interaction is key to keeping a positive mindset throughout the office and even more so for employees working at home. Companies are hiring more remote employees, expanding across the country and even the globe. While this leverages several benefits, it also can create some challenges in developing an inclusive company culture and connected dynamic. All of the capabilities 5G will introduce into your business play a role in how you’ll connect and interact internally, no matter your organization’s geographical location. Trust us, boring conference calls will be a thing of the past as the potential of 5G innovations expand to holographic calling, enabling users to view 3D presentations with or without glasses, and interactive meetings utilizing AI technology. Why would you choose to use small chat boxes on computer screens when augmented and virtual reality connectivity will run seamlessly?
It’s clear to see that the power and innovation 5G is bringing will revolutionize the way people do business in a big way. Here at Blue Signal, we plan to utilize many of these advancements in multiple aspects of our business. One area we are excited to embrace is the ability to further empower our remote employees’ flexibility in where and how they work. Blue Signal has a long history of leveraging a geographically diverse team as we’ve had recruiters working from all over the country since our inception. The ability to further advance the way we communicate and engage with each other internally will be a huge initiative in the coming year as we look forward to continuing to nurture our tight-knit company culture. Additionally, the connectivity and seamless functionality of 5G will allow us to better serve our clients and candidates. As the recruiting industry continues to grow, we continue to stay committed to rising above the norm by utilizing the most effective resources, technology, and processes available to us. Reach out to one of our recruiters today to talk about what 5G advancements mean for your workforce and how you can capture these benefits.
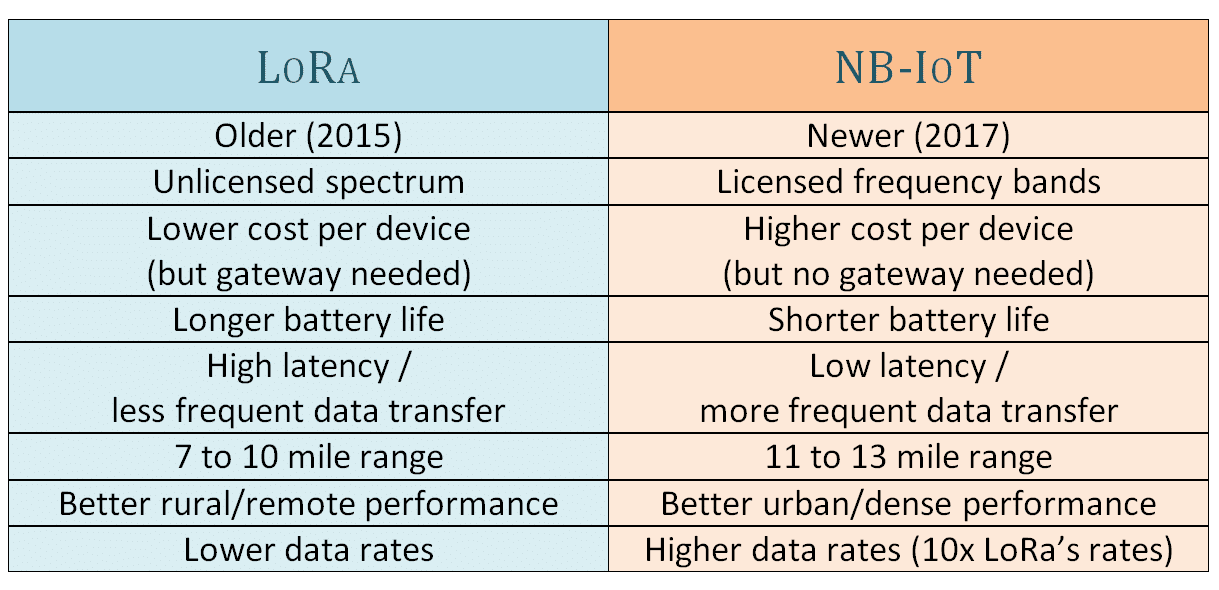
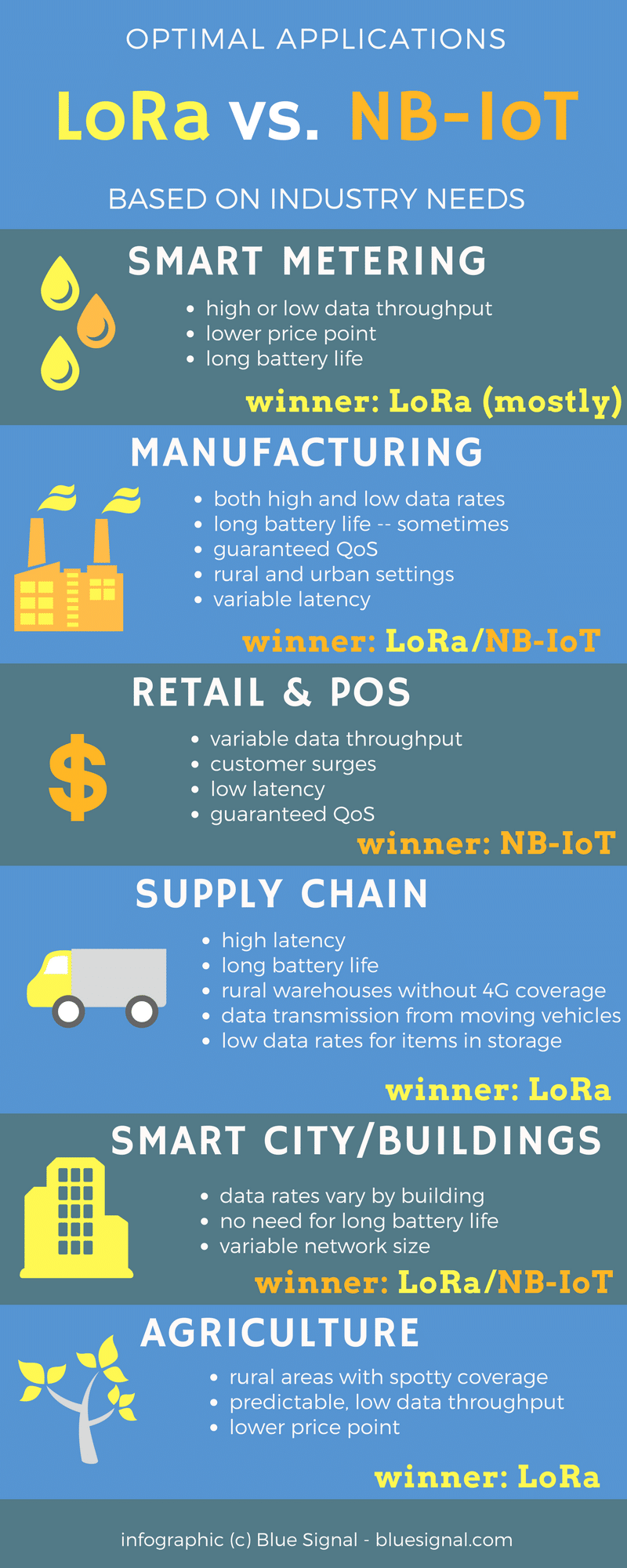
 LPWAN stands for Low-Power Wide Area Network, a wireless network designed to efficiently connect smart devices across long distances, usually through a low bit rate. LPWANs are ideal for IoT devices that don’t need to manage large amounts of data, or for circumventing more expensive gateway technology. This can include smart meters, consumer products, and sensors. The overall value of the LPWAN market is expected to reach $25 billion within 4 years.
LPWAN stands for Low-Power Wide Area Network, a wireless network designed to efficiently connect smart devices across long distances, usually through a low bit rate. LPWANs are ideal for IoT devices that don’t need to manage large amounts of data, or for circumventing more expensive gateway technology. This can include smart meters, consumer products, and sensors. The overall value of the LPWAN market is expected to reach $25 billion within 4 years.