Our world continues to become more interconnected than ever due to the innovative advancements in telecommunications. All types of industries are collaborating to deliver disruptive technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and smart homes – making it crucial for those beyond the telecom space to understand this high-tech terminology. Each of our lives are influenced by our ability to connect with others, whether you work in finance, recruiting, manufacturing, healthcare, or even agriculture. Something as simple as Wi-Fi is a tool delivered by the telecom industry that we all need to do our jobs, no matter the field. According to market analysis, the telecom industry is predicted to grow 5.4% annually between 2021 and 2028. That’s a faster growth rate than the automotive, construction, insurance, and agriculture industries! No wonder it’s been hard to keep up with the ever-changing telecom terms.
To shed some light on this industry jargon and bring you up to speed on some recent advancements, Blue Signal created a glossary of the most common and useful telecom terms. These telecom terms will help you better understand what goes into keeping us all connected – and possibly provide some knowledge to help you stand out with a future client or employer. Read on to learn about 5G, VPNs, TCP/IP, and more. For the full list of 80+ telecom terms, click the link below to download our guide.
Top 20 Telecom Terms:
- 3G/4G/5G: Third-, fourth-, and fifth-generation wireless capabilities that allow for faster and broader access to information and services via mobile devices.
- Bandwidth: The range of frequencies in a communication channel. Analog communications measure bandwidth in Hertz, whereas digital communications use bits per second (bps).
- Broadband: A high-capacity transmission technique that allows for the communication of a large amount of information over a wide range of frequencies.
- Carrier: Vendor of transmission services operating under terms defined by the FCC as a common carrier. Owns a transmission medium and rents, leases, or sells portions for a set tariff to the public via shared circuits. (AT&T, Sprint, MCI, Ameritech, etc.)
- Fiber Optic Cable: Glass strands used to transmit light signals for cell phone and Internet connections. These cables allow for connection speeds 10 to 100 times faster than copper wire.
- Firewall: A barrier device placed between two separate networks. A firewall can be implemented in a single router that filters out unwanted packets or it can use a variety of technologies in a combination of routers and hosts. Today, many firewalls combine filtering functionality with Network Address Translations (NAT) functions.
- Gateway: A network element that performs conversions between different coding and transmission formats. The gateway does this by having many types of commonly used transmission equipment and/or circuits from different carriers to provide a means of interconnection.
- Local Area Network (LAN): A group of computer and peripheral devices that are connected in a limited area such as a school, laboratory, home, or office building.
- Network: Any connection of two or more computers that enables them to communicate. Networks may include transmission devices, servers, cables, routers, and satellites. The phone network is the total infrastructure for transmitting phone messages.
- Open Network Architecture (ONA): The overall design of a carrier's basic network facilities and services to permit all users of the basic network, including enhanced service providers, to interconnect to basic network functions on an unbundled and "equal access" basis.
- Private Branch Exchange (PBX): A private telephone exchange that serves a particular organization or business and has connections to the public telephone network. Newer PBXs have features that allow for data and video communications as well as voice.
- Radio Frequency (RF): A measurement representing the oscillation rate of electromagnetic radiation spectrum, or electromagnetic radio waves, from frequencies ranging from 300 GHz to as low as 9 kHz. With the use of antennas and transmitters, an RF field can be used for various types of wireless broadcasting and communications.
- Router: A device or setup that finds the best route between any two networks, even if there are several networks to traverse. Like bridges, remote sites can be connected using routers over dedicated or switched lines to create WANs.
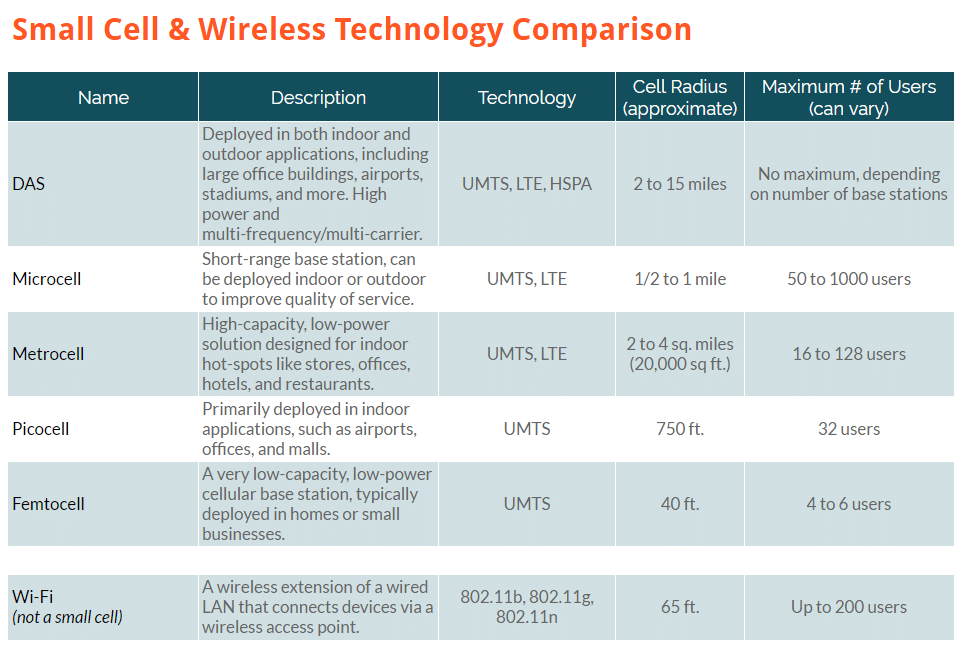
- Small Cell: An umbrella term used to describe a miniature radio access point (AP) or wireless network base station with a low radio frequency (RF) power output, footprint, and range. They enhance cellular network coverage and capacity in areas where use demands are the highest.
- Switch: A mechanical or solid-state device that opens and closes circuits, changes operating parameters, or selects paths for circuits on a space or time division basis.
- Telecommunications: Communicating over a distance. Use of wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic channels to transmit and receive signals for voice, data, and video communications.
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internetworking Protocol (TCP/IP): A protocol developed to allow dissimilar devices to communicate across many kinds of networks.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): VPN modules create closed secure tunnels for communication between two firewalled LANs. VPN technology is a common approach used today for providing secure communications over IP networks.
- Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP): Telephone services provided over broadband Internet connections rather than traditional phone networks.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): An important computer network that is spread across a large geographical area. WAN network systems could be a connection of a LAN that connects with other LANs using telephone lines and radio waves.
As this global tech trend advances, the telecom industry will continue to be involved in all things that keep us connected. Impacting all different types of industries, it’s more important now than ever to stay up to speed on what these telecom terms mean.
Whether you’re trying to stay relevant in your current field, or are looking to break into a new career path, Blue Signal has the resources to help. Our recruiters are specialized in their industries and understand the importance of knowledge-share across these diverse fields. Reach out today to learn more about how you can stand out in your industry and reach your career goals.