The Internet of Things has enjoyed top buzzword status for a while now, but the technology has made steady strides away from the hype and towards a tangible, profitable reality. Here are the top trends of IoT since the start of 2017:
1. 3GPP Standardization of NB-IoT (Narrow-Band IoT) for LPWAN
NB-IoT technology took a leap forward last month when Cisco and Optus announced at Barcelona’s MWC they have completed live trials of NB-IoT technology on the Cisco Jasper platform. Most new connected devices are expected to launch on an LPWAN (Low Power Wireless Access Network) platform, especially inexpensive devices that use low levels of power and large ranges (smart umbrellas and toasters, for example).
NB-IoT is shorthand for Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT, also called LTE-M2). It is a radio technology standardization proposal developed by Huawei, Ericsson, Qualcomm, Vodafone, and other telecom heavy hitters. The Internet of Things is made up of hugely diverse smart devices—from airplanes to bracelets. To improve interoperability, NB-IoT was designed to allow many different types of devices and connectivity services to connect over cellular telecom bands—not just smartphones and tablets. Read more about NB-IoT here.
2. Connected Cars & Self-Driving Technology
CES 2017 was dominated by connected cars and related self-driving technology, with over 1000 exhibitors featured vehicle technologies or accessories. Tesla investors worried last year that self-driving technology would take a nosedive after one of their test drivers was killed last year in a fatal crash. However, commercial and private interest has grown by leaps and bounds. Uber got an early lead in the driverless tech race when it began testing driverless cars late last year in Phoenix, Pittsburgh, and San Francisco. Despite setbacks when a driverless car crashed in Arizona this month, the program is back on track. Google, Ford, and GM have also been testing self-driving technology in the United States.
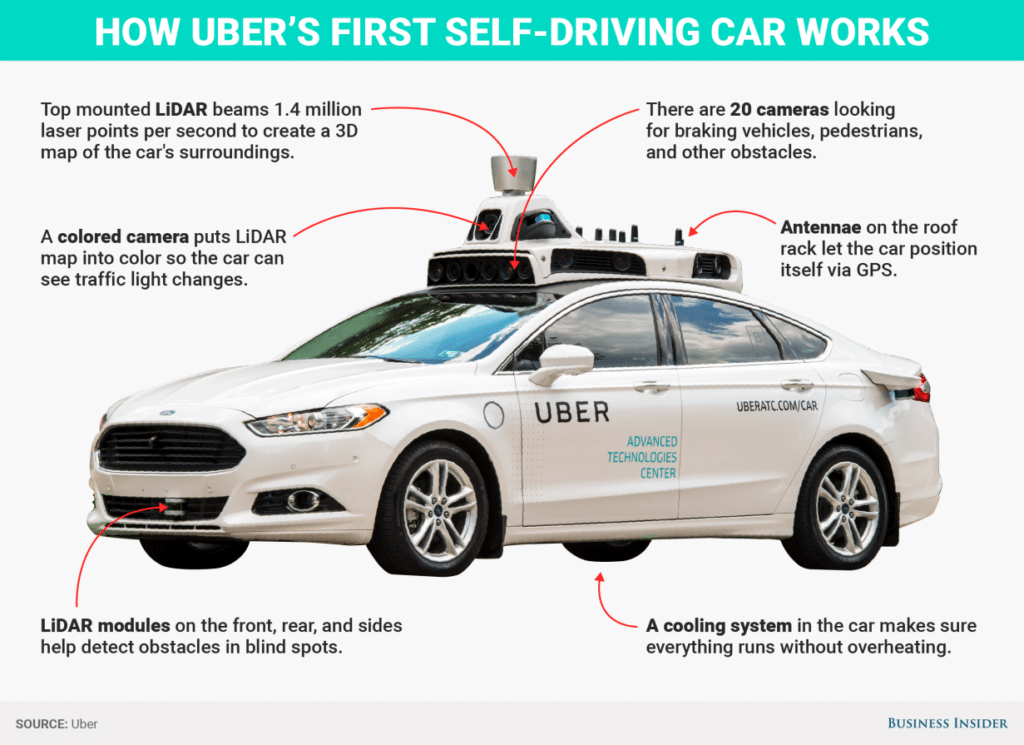
Image credit: Business Insider
Intel is the biggest newcomer to the driverless technology arena. In a $15 billion deal on March 14, it purchased Mobileye, an OEM for driverless vehicle sensors and cameras. Uber’s driverless vehicles use a sophisticated combination of roof-mounted LiDAR sensors and color cameras to interpret the road. Intel is expected to scale similar digital vision technology components to sell to automakers that cannot make the huge investment necessary to develop the technology in-house.

Image: At CES 2017, Divergent 3D unveiled the Blade, a 3D-printed connected car.
In the connected car software arena, AT&T boasts that it already connects 11 million cars on its network. Cisco’s Jasper IoT software now supports 50 vehicle brands, including Honda’s proprietary MyHonda Connected Car platform. Cisco has had many wins in the IoT arena with its Jasper platform, releasing smart solutions for fleet management, connected buildings, industrial equipment, and more. Over 9000 companies and 40 million smart devices run on Jasper’s Control Center software, with millions of devices being added every month.
5G Advancements
At Mobile World Congress 2017, South Korean carrier KT announced that it will have the world’s first commercially viable 5G network by 2019. While this is many years away from reality, many service providers are shifting discussions away from features to talk about standardization opportunities. Without a concerted standardization effort, 5G will likely take much longer to launch and be slower to grow once it does.
Ericsson recently launched its “5G for India” program to conduct 5G testing and ecosystem development in India. Many governments are considering their options for modernizing infrastructure to prepare for 5G, including China, the UK, and Thailand. Any country that gets an early lead in 5G availability will likely enjoy an economic leg-up over less connected countries. The challenge is that many infrastructure must be built from scratch, especially in countries with large rural areas.
IoT Security
Due to last October’s massive DDoS attack that used IoT device back doors to cause massive service outages, security is a top priority in the IoT space. Authentication and device-specific security are improving, but Sanjay Khatri, director of product marketing for IoT Services at Cisco, says that IoT security “takes a village.” If the network is secure but hackers can penetrate the device itself, the security chain has failed. Security is necessary at every link of the IoT value chain.
Information security is an escalation war, and providers at all levels are racing to protect IoT devices and applications against digital attacks. One of the most important IoT security measures already in use is REST-based APIs, which protects the movement of data between devices, applications, and back-end systems. Many device manufacturers are building two-step or even three-step authentication features into their devices. Instead of a single password, many connected things use biometrics (like a fingerprint) or digital certificates in addition to passwords and PINs. Beyond the device layer, cloud platforms like Cisco Jasper rout the data through VPN tunnels to prevent DDoS and similar network-wide outage attacks.
Have a hiring need or questions about the IoT industry? Contact us for a free consultation at info@bluesignal.com.